备忘录模式
定义
在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该状态之外保存这个状态。
这样以后就可以将该状态恢复到原来保存的状态。
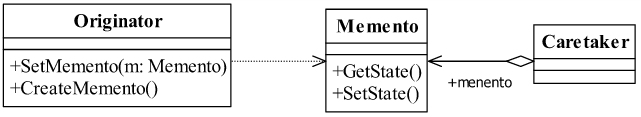
实现
Originator
发起人角色,记录当前时刻的内部状态,负责定义哪些属性备份范围的状态,负责创建和恢复备忘录数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| public class Boy {
private String state = "";
public void change(){
this.state = " I Am So Sad.";
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public Memento createMemento(){
return new Memento(this.state);
}
public void restore(Memento memento){
this.setState(memento.getState());
}
}
|
Memento
备忘录角色,负责存储Originator发起人对象的内部状态,在需要的时候提供发起人需要的内部状态。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class Memento {
private String state = "";
public Memento(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
}
|
Caretaker
备忘录管理员角色,对备忘录进行管理、保存和提供备忘录。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class Caretaker {
private Memento memento;
public Memento getMemento() {
return memento;
}
public void setMemento(Memento memento) {
this.memento = memento;
}
}
|
Use
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| Caretaker caretaker = new Caretaker();
caretaker.setMemento(boy.createMemento());
System.out.println("Now Boy Is : " + boy.getState());
boy.change();
System.out.println("Now Boy Is : " + boy.getState());
boy.restore(caretaker.getMemento());
System.out.println("Now Boy Is : " + boy.getState());
|
使用场景
- 需要保存和恢复数据的相关状态场景
- 提供一个可回滚的操作
- 需要监控的副本场景中
- 数据库连接的事务管理
注意事项
- 备忘录的生命周期
主动管理备忘录的生命周期,不实用就需要立即删除其引用。
- 备忘录的性能
要控制备忘录的历史记录数量,以及大对象的备忘录。
扩展
Clone方式的备忘录
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| public class Originator implements Cloneable {
private String state = "";
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public Originator createMemento(){
return this.clone();
}
public void restoreMemento(Originator originator){
this.setState(originator.getState());
}
@Override
protected Originator clone() {
try {
return (Originator)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class Caretaker {
private Originator originator;
public Originator getOriginator() {
return originator;
}
public void setOriginator(Originator originator) {
this.originator = originator;
}
}
|
多状态的备忘录模式
把整个对象转换成Map,当然也可以序列化、或者直接复制整个对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class Memento {
private HashMap<String,Object> stateMap;
public Memento(HashMap<String, Object> stateMap) {
this.stateMap = stateMap;
}
public HashMap<String, Object> getStateMap() {
return stateMap;
}
public void setStateMap(HashMap<String, Object> stateMap) {
this.stateMap = stateMap;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| import java.beans.BeanInfo;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class BeanUtils {
public static HashMap<String,Object> backupProp(Object bean){
HashMap<String,Object> result = new HashMap<>();
try{
BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(bean.getClass());
PropertyDescriptor[] descriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
for (PropertyDescriptor descriptor : descriptors) {
String fieldName = descriptor.getName();
Method getter = descriptor.getReadMethod();
Object fieldValue = getter.invoke(bean, new Object[]{});
if (!fieldName.equalsIgnoreCase("class")){
result.put(fieldName, fieldValue);
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static void restoreProp(Object bean, HashMap<String,Object> propMap){
try{
BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(bean.getClass());
PropertyDescriptor[] descriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
for (PropertyDescriptor descriptor : descriptors) {
String fieldName = descriptor.getName();
if (propMap.containsKey(fieldName)){
Method setter = descriptor.getWriteMethod();
setter.invoke(bean, new Object[]{propMap.get(fieldName)});
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| public class Originator {
private String state1 = "";
private String state2 = "";
private String state3 = "";
public String getState1() {
return state1;
}
public void setState1(String state1) {
this.state1 = state1;
}
public String getState2() {
return state2;
}
public void setState2(String state2) {
this.state2 = state2;
}
public String getState3() {
return state3;
}
public void setState3(String state3) {
this.state3 = state3;
}
public Memento createMemento(){
return new Memento(BeanUtils.backupProp(this));
}
public void restoreMemento(Memento memento){
BeanUtils.restoreProp(this, memento.getStateMap());
}
}
|
多备份的备忘录
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class Caretaker {
Map<String, Memento> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
public void backup(String version, Memento memento){
map.put(version, memento);
}
public Memento get(String version){
return map.get(version);
}
public Map<String,Memento> getAll(){
return this.map;
}
}
|
优雅的实现
Bean 对象专注自己的业务,不需要关心备份和恢复业务。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class Original implements Cloneable {
private String state;
private String info;
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public String getInfo() {
return info;
}
public void setInfo(String info) {
this.info = info;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
|
备份管理员负责版本的备份与恢复工作,职责明晰。
同时要注意历史版本次数,防止版本过多。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public class Caretacker {
private int size = 10;
private Map<String, Original> histo = new LinkedHashMap<>();
public boolean backup(String key, Original o) {
if (histo.size() >= 10) {
return false;
}
try{
histo.put(key,(Original) o.clone() );
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
public Original get(String k) {
return histo.get(k);
}
}
|
