什么是事务Transaction
Transaction一词在英语的翻译中还有一次交易、业务、事务、办理、处理;
对于一次账户充值100元的操作,其中就有多个环节。
1)检查账户的有效性,查询账户余额;
2)记录充值流水;
3)为账户余额增加100元。
对于这三个操作来讲,他是一个Transaction, 要么都成功,只要有一个失败,就必须整个Transaction失败,不允许记录了充值流水成功,但是余额增加失败。这三个是一个整体,是不可分割的工作单元。
事务的特性
原子性 Atomic:要么都成功,只要有一个步骤失败,整个步骤必须回滚(失败)。
一致性 Consistency:事务保证读取到的数据总是一致的,如(不存在100元的充值流水时金额为100元, 存在100元的充值流水时金额为200元)。
但是对于这个充值过程来讲,肯定是先记录了充值记录,后增加100元余额。可以查到充值记录,但余额是100是客观存在的。
隔离性Isolation:为了保证一致性,事务执行过程中的中间状态不对外部可见,事务需要对整个过程进行隔离。
持久性 Durability:只要事务一经提交,就一定会被持久化到磁盘中。
Transaction 阶段
Transaction 需要有开始和结束,标记一个Transaction的开始和截止;
当所有的操作都成功的时候,需要Commit;
当其中某个操作失败的时候,之前的操作需要Rollback;
Transaction Start;
Transaction Commit Or Rollback;
Transaction End;
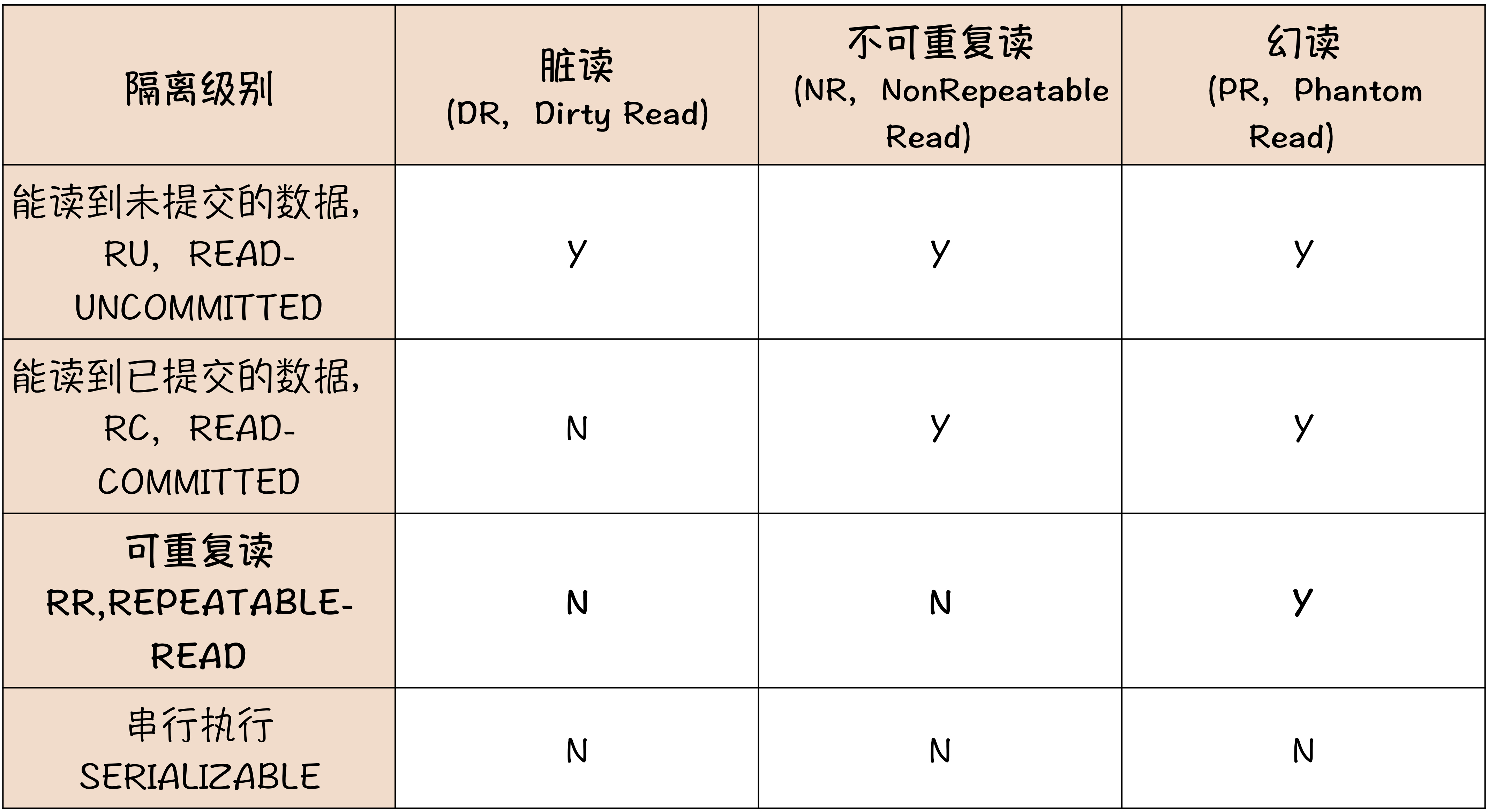
脏读
假如业务员给账户A增加100元的操作的同时(记录了充值流水100元,流水号为666),对账系统也在同时运行同时读取到了这一笔流水号为666的流水记录。但是后续的为余额增加100元的操作失败了,整个Transaction RollBack。 导致账户余额比对账系统少了100元。
在这里,对账系统看到了业务系统Transaction未提交时的数据,叫脏读。
也就是说当前事务的中间状态,对其他事务时可见的。
事务的最低隔离级别是未提交读(Read Uncommitted),因此会发生脏读的现象。
为了解决脏读的现象,需要将事务隔离起来,只允许读到已提交的数据。 Read Committed.
不可重复读
假如业务员A给用户增加100元。
开启事务;
查询账户余额 100元;
有其他事情去忙……
此时业务员B也给用户增加100元。
开启事务;
查询账户余额 100元
增加流水记录;
增加账户余额100元,变为200元;
结束事务;
业务员A回来为A增加100元:
查询账户余额 200元;
不可重复读就是业务员A在同一个事务内,先后两次读取同一条数据的结果可能不一样。
可重复读就是业务员A在同一个事务内,先后两次读取同一条数据的结果总是相同的,无论其他会话是否已经更新了这条数据。
为了保障在同一事务下,先后两次读取到的同一条数据结果一致,需要将事务的隔离级别调整为可重复读(Repeatable Read)。
幻读
假如业务员A给用户增加100元。
开启事务;
查询流水中是否有ID为1000的流水记录,不存在;
业务员B给用户增加100元;
开启事务;
查询流水中是否有ID为1000的流水记录,不存在;
插入流水记录;
更新账户余额为200;
提交事务;
业务员A开始执行;
插入流水记录,此时已经有ID为1000的流水记录,系统异常;
可以开启重试机制;
由于隔离性,查询是否有ID为1000的流水记录时还是不存在,重试插入时还是异常。
为了解决幻读的问题,需要将所有的事务和操作进行串行化。这也是Database的最高隔离级别,性能也最差。
对于账户充值来讲,交易的原子性以及持久性是最重要的。可以适当牺牲一些一致性和隔离性。
以下操作在 ReadCommitted 和 Repeatable Read下是安全的。
1)给账户余额表增加一个log_id属性,记录最后一笔交易的流水号。
2)首先开启事务,查询并记录当前账户的余额和最后一笔交易的流水号。
3)写入流水记录。
4)更新账户余额以及流水记录ID,需要在更新语句的Where条件中限定,只有流水好等于之前查询出的流水号时才能更新。
update account_balance set amount = amount + 100 , log_id = 2 where user_id = 0 and log_id = 1;
5)检查更新余额的返回值,如果为1 提交事务,否则回滚。